FAQ Get, update GIT Projekt Quellen
Hier finden Sie Informationen darüber, wie Sie die Quellen des Dolibarr-Projekts erhalten können. Es werden mehrere Methoden beschrieben, aber wir empfehlen, die auf GitHub basierende Methode zu verwenden.
Letzte Version der Quellen durch tgz-Download abrufen
Diese Methode kann auch von nicht-technischen Benutzern verwendet werden. Sie ermöglicht es Ihnen, die Quellen des Hauptentwicklungszweigs (HEAD genannt) zu erhalten, indem Sie einfach eine Datei herunterladen: Diese Operation besteht darin, die letzte Version der Dolibarr-Dateien zu erhalten, die jede Nacht in eine tgz-Datei gepackt werden. Die Datei ist über einen Link verfügbar:
Last GitHub snapshot of Dolibarr source files.
Neue Dateien überschreiben alte Dateien. Der Nachteil dieser Methode ist, dass Sie das Paket jedes Mal herunterladen und dekomprimieren müssen, wenn Sie Updates erhalten möchten.
Entwickler sollten diese Methode nicht verwenden, um Quellen zu erhalten, sondern die nächste.
Letzte Version der Quellen über einen anonymen GIT-Zugang abrufen
Sie können diese Methode verwenden, wenn Sie keinen GIT-Zugang haben. Mit dieser Methode können Sie keine Änderungen einreichen. Wenn Sie also ein Entwickler sind, sollten Sie ein GitHub-Konto erstellen und die nächste Methode anstelle dieser Methode verwenden.
Voraussetzungen
- Mit Eclipse IDE
Zuerst müssen Sie eine funktionierende Installation von Eclipse haben. Das EGit-Plugin muss ebenfalls installiert worden sein. Verwenden Sie dazu den Find And Install process im Eclipse Menü, fügen Sie die GIT update URL hinzu:
https://download.eclipse.org/egit/updates
Wählen Sie dann EGit zur Installation aus (JGit muss nicht ausgewählt werden)
- Mit der GIT-Kommandozeilen-Client-Schnittstelle
Sie müssen den GIT-Client installieren (das GIT-Befehlszeilentool wird unter Linux mit "sudo apt-get install git" installiert, für Windows ist der GIT-Client unter https://git-scm.com/download/win zu finden).
Clone Prozess
Geben Sie zunächst den Wert des Repositorys mit den Referenzquellen in Ihr GIT-Client-Tool ein.
- Mit Eclipse, gehen Sie in die Perspektive GIT, klicken Sie auf den Button "GIT Repository klonen". Geben Sie die GIT-URL des Projekts ein, das Sie erhalten möchten.
git://github.com/Dolibarr/dolibarr.git (read only)
oder wenn Sie einen Fork von dolibarr github von der github-Weboberfläche erstellt haben
git@github.com:yourgitaccount/dolibarr.git (read and write access)
Ihr Eclipse-GIT-Client wird Sie auffordern, die Branches auszuwählen, an denen Sie interessiert sind. Branches, die jetzt noch nicht ausgewählt sind, können später durch einen "Fetch" aus der "Remotes"-Ansicht ausgewählt werden, aber versuchen Sie, nur den Branch auszuwählen, den Sie benötigen. Dies erspart Ihnen später Zeit und Probleme.
Hinweis: Wenn Sie sich hinter einer Firewall befinden, müssen Sie die Eclipse-Proxy-Zugangsdaten im Eclipse-Menü Fenster - Einstellungen - Allgemein - Netzwerkverbindung einstellen und die alternative URL verwenden:
https://gitlogin:gitpassword@github.com/yourgitaccount/dolibarr.git
- Mit GIT auf der Befehlszeilenschnittstelle:
Richten Sie zunächst Ihren Git-Client ein:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "user@domain.com"
git config --list
Dann klonen Sie das Repository lokal:
git://github.com/Dolibarr/dolibarr.git (nur lesen)
oder wenn Sie einen Fork von dolibarr github von der github-Weboberfläche erstellt haben
git@github.com:yourgitaccount/dolibarr.git (Lese- und Schreibzugriff)
Hinweis: Wenn Sie sich hinter einer Firewall befinden, müssen Sie Ihre Proxy-Informationen einstellen und die alternative https-URL verwenden:
git config --global http.proxy http://proxyuser:proxypass@proxyserver:proxyport
git clone https://gitlogin:gitpassword@github.com/yourgitaccount/dolibarr.git dolibarr
Sobald dieser Schritt bestätigt ist, lädt Ihr GIT-Client alle Dateien vom entfernten GIT-Server herunter. Dies kann einige Sekunden oder Minuten dauern.
Sobald der Download abgeschlossen ist, müssen Sie wählen, an welchem Zweig Sie arbeiten möchten.
- Mit GIT auf der Befehlszeilenschnittstelle;
git checkout develop
git checkout x.y
Dadurch wird eine lokale Branche erstellt und automatisch ein Checkout durchgeführt.
- Klicken Sie in Eclipse mit der rechten Maustaste auf "Branches - Remotes -" die Branche, die Sie lokal duplizieren möchten".
Wählen Sie " Erstelle Branch" (und markieren Sie das Kästchen "Checkout"). Dadurch wird der Inhalt der Branche dupliziert, um lokal daran zu arbeiten, und Ihr "Arbeitsverzeichnis" wird aktualisiert, um an dieser Branche zu arbeiten.
Erstellen Sie ein Eclipse-Projekt:
Wenn Sie Eclipse verwenden, erstellen Sie, sobald die Verzweigung lokal erstellt wurde, ein PHP-Projekt aus dem Assistenten, indem Sie "Create from existing project" wählen und das Verzeichnis auswählen, das Ihr lokales GIT-Repository ist (Wählen Sie nicht die Option, ein PHP-Projekt komplett neu zu erstellen).
Klicken Sie dann mit der rechten Maustaste auf das Projekt in Ihrem Eclipse-Arbeitsbereich und wählen Sie "Team - Share". Wählen Sie GIT und klicken Sie auf die Option "Use or create repository in parent folder of project". Eine alternative Methode ist File->Import, Git->Project von Git, Wählen Sie das Git-Repository und Weiter, Assistent für neue Projekte verwenden -> Php-Projekt, geben Sie den Ordner Ihres lokalen GIT-Repositorys ein.
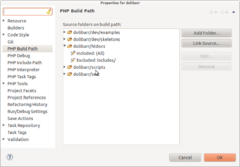
Dann können Sie Eclipse so einstellen, dass es nicht alle Projektdateien für seine Build-Tools (Outline Scanner, TODO Scanner, Syntax Scanner...) scannt. Dies verhindert, dass Eclipse zu langsam ist. Klicken Sie dazu mit der rechten Maustaste auf das Projekt, wählen Sie Build Path und stellen Sie es wie im folgenden Screenshot ein.
Get last version of sources using a GitHub user access
Prerequisite
- With Eclipse IDE
You must before create an account on GitHub (https://github.com/) and upload a public RSA or DSA certificate into your account profile.
Then, you must have a working install of Eclipse. EGit plugin must also have been installed. For this, use the Find And Install process into Eclipse menu, add the GIT update URL:
https://download.eclipse.org/egit/updates
Then choose to install EGit.
- With the GIT Command Line Client Interface:
You must before create an account on GitHub (https://github.com/) and upload a public RSA or DSA certificate into your account profile.
Then, you need to install GIT client (GIT command line tool with Linux installed with "sudo apt-get install git", or the GIT client for Windows found at https://git-scm.com/download/win).
Fork process
Login to Github, with login you created in previous step. Then go onto page
https://github.com/Dolibarr/dolibarr
And click on button "Fork".
This will create a copy (a fork) of project into your own github area. Because you will be the owner of this fork, you will have all permissions on it to be used in next steps.
Clone process
Then process is same as getting sources with anonymous access.
URL to use for GIT clone is same:
git@github.com:YourGitHubLogin/dolibarr.git
Note that a HTTPS URL is also available but it's sometimes offline (so prefer using first one, link with HTTPS is required only if you are behind a firewall):
https://yourgithublogin@github.com/Dolibarr/dolibarr.git
Update your repository
To update your local workspace:
- With Eclipse IDE:
right click on Eclipse project and select "Pull".
If you made some changes into your Eclipse workspace on files that were changed into the GIT remote reference, your GIT client will make a merge automatically.
- If there is conflicts, the merge will mark all conflict files as "conflict" (See later to solve this state).
- If not, you will get all new version files including all your changes.
If you already have commited some files into your local repository, your workspace will be marked as "Merged". All you have to do is make a commit to validate your local repository as including your changes and changes made by others.
- With the GIT Command Line Client Interface:
git pull
Commit and publish your changes
To see all changes you made into your working directory and waiting to be added into Git:
- With GIT Command Line Interface:
git status
git diff subdir/filename
To add changes made into your local repository into the GIT index, then commit this index :
- With Eclipse: Right click on file or directory to commit. Select file to add/remove/update into commit.
- With GIT Command Line Interface:
git commit -a -m "Commit text"
This will save add and changes into your local branch.
To push them on the GIT repository server,
- With Eclipse: right click on project and choose "Team - Push to Upstream".
- With GIT Command Line Interface:
git push
To cancel a commit:
- With GIT Command Line Interface, if commit was not already pushed:
git reset --soft HEAD~1
- With GIT Command Line Interface, if commit was already pushed:
git revert IdCommit or git revert HEAD (for last commit)
To merge changes done into your forked GIT instance into official Dolibarr instance:
- Go into GitHub web interface of your forked Git instance.
- Click on small button "Create a Pull request".
- Choose commit you request inclusion and validate.
Ask official project to include your changes
Once you pushed one or several commit toward your distant fork area on github, you can ask the Dolibarr core team to include it into official project. For this, follow this tutorial: https://help.github.com/articles/creating-a-pull-request/
Add an external commit into current repository
Some developers may work and do commit into their own Git repository after forking the project. If you are interesting into getting this changes, you can import them with the following steps.
You need both Eclipse and GIT Command Line interface to achieve this:
- First, go into GIT setup view and right click on "Remotes" of your Eclipse Git working space and choose "Create a remote..."
- Type name or remote fork the developer has create (in most cases, it's developer Git login). For example: "thedevlogin". Choose also "Configure Fetch".
- Type URI of Git repository of developer. For example: git://github.com/thedevlogin/dolibarr.git. Also add a refspec value to declare the branch you want to get. For example: refs/heads/master:refs/remotes/thedevlogin/master. Click "Save and Fetch". A new entry will be added into "Remote Tracking" making possible to read/get commits done into this branch.
Now, go on command line of your git repository (in most cases on Linux, it's /home/yourlogin/git/yourdolibarr) and type the git cherry-pick command:
git cherry-pick -x commitid
where commitid is value of commit id you want to get.
Once this is done, go back to Eclipse and make a refresh on project. You will see modified files appears with decorators (with conflicts if there is).
It the cherry-pick fails because of conflicts, you can cancel the cherry-pick try with
git cherry-pick --abort
Solving a conflict
If a file has been marked as "conflict" after a Pull, open the file to edit it. Find string "<<<<<<<<<<", you will see part of code that is conflict between "<<<<<<<<<" and ">>>>>>>>". Edit manually code lines and remove "<<<<<<<<" and ">>>>>>>".
Then, right click on file and select "Add".
If you prefer to forget completely all changes you made into all files (so to restore you workspace with content of remote repository), you can make a hard reset:
- With Eclipse: Right click on project top line and select "Reset" then "Hard" then "Reference - HEAD".
- With GIT Command Line Interface: You can achieve this with command
git reset --hard HEAD
To reset changes you commited but not pushed to origin
git reset --hard origin/develop
Tagging sources
With GIT Command Line Interface:
To add a tag to a current version:
git tag -a -m "Release|Maintenance release x.y.z" "x.y.z"
or
git tag -a -f -m "Beta x.y.betai" "x.y.betai_YYYYMMDD" idcommit # -f force if an existing tag already exists, idcommit allows to choose commit to tag
git push --tags # To push tags to remote origin
To remove a tag:
git tag -d "x.y.z_YYYYMMDD"
git push remoteentryname :x.y.z_YYYYMMDD # To validate delete on remote origin
Creating a new branch
With GIT Command Line Interface:
Create a clone (see previously) of the branch from where you want to create another branch, then go into directory and launch command:
git branch x.y
git push origin x.y
With Eclipse:
Create a clone (see previously) of the branch from where you want to create another branch, with a checkout done. The go into view git. Choose branches, remote tracking and select start branch. Right click and choose "Create branch". Then make a push to create branch remotely. Then go into "Remotes - origins" and edit the entries to pull and push onto new branch. It may also be required to edit the .git/config file to have project linked by default onto new branch.
Deleting a branch
With GIT Command Line Interface:
Do a push on branch but add : before name of branch:
git push remoteentryname :branchnametodelete
Merging a maintenance branch x.x into dev branch
With Eclipse:
- Go onto the root directory of project with a checkout of the dev branch.
- Check fetch setup to be sure, this repository contains both information of dev branch and version x.x you want to merge.
- Right click onto root directory and choose "Team - Merge". Select "x.x". Click onto "Merge options - Commit", because we want to commit merged branch if there is no conflicts.
- Once merge is done, check everything is ok.
- Commit and push.
Pushing a branch onto another Git server
You may want to synchronize another GIT server. To synchronize push to another server, this is how to proceed. With Eclipse:
- Go onto Git clone view and add a remote with a name, choose "Configure push" and enter URL. For example, for name "sourceforge" and URL "ssh://yoursourceforgelogin@git.code.sf.net/p/dolibarr/code"
- Just validate, a first push will be done automatically.
- To force sync, run
git push sourceforge develop
git push --tags sourceforge develop
Statistics
With GIT Command Line interface:
To count number of changes developers have made between a version x and y:
- First, search commit id of tags you want to compare
To find id_start (common commit id between 2 versions/tags)
git merge-base refs/tags/3.3.0 origin/3.4
or
git merge-base 3.7 origin/develop
To find id_end, choose among
git show-ref
Choose a value for id_start and id_end Note: id_end can be HEAD.
- Then run git log to have list of all changes from last common commit to last commit
git log id_start..id_end
- To get total number of added/deleted lines:
git log --ancestry-path --numstat --pretty="%H" id_start..id_end | awk 'NF==3 {plus+=$1; minus+=$2} END {printf("+%d, -%d\n", plus, minus)}'
To count number of changes finally between a version x and y (it differs from previous count because in previous count, a change can be done 2 times at two different moment to change differently. With second method, you count changes finally found if changes were ok at first try).
- Use same method than previously but instead of running git log, run git diff.
git diff -b -M --numstat --pretty="%H" id_start..id_end | awk 'NF==3 {plus+=$1; minus+=$2} END {printf("+%d, -%d\n", plus, minus)}'
More information in GIT usage is available here.